Return
to IFS 110 class Notes Menu!

Project 1
Building an
Application
What is Visual
Basic?
- Visual Basic is itself a
Windows Application
- Function: builds special- purpose Windows
Applications
- Uses Graphical User Interface (GUI) of Windows in the
development
process
- Stand-alone
application - an EXE,
one that runs independently of Visual Basic
Active Window
3 Windows in
Visual Basic
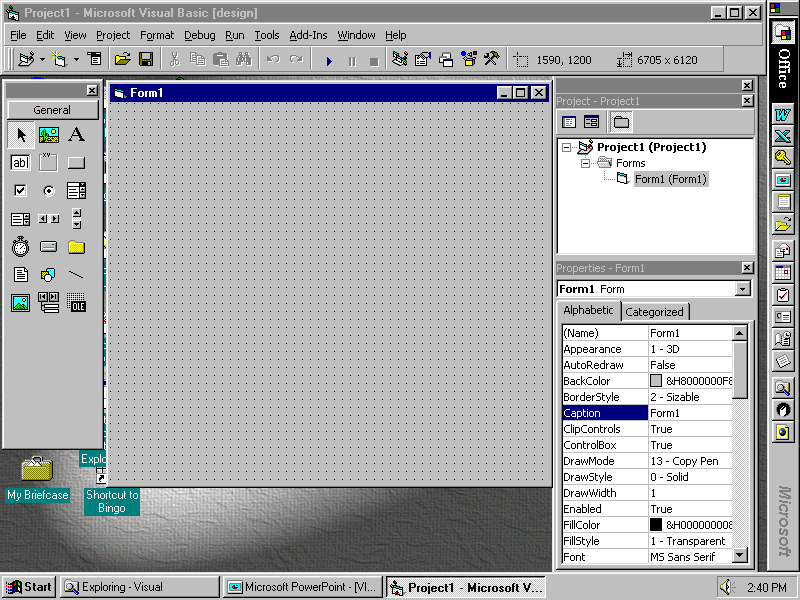
- Form Window
- user interface
- Project Window - codes for forms and modules
- Properties Window - properties of objects on the form (defaults)
Setting
Development Environment Options
- With VB6 can
build desktop applications,
application components, and Internet
applications
- When VB6
started, choose to open a recent, existing,
or new project (must specify
type of new project) (usually Standard EXE project type)
Types
of Interfaces
Note: Interface chosen is a personal preference
Types
of Interfaces
- VB6 records the size and location
of these windows when project is closed
so that its integrated development environment
(IDE) display the same each time you
start Visual Basic
Problem in Lab : IDE
may look
completely different every time
student comes to lab and starts Visual Basic
Arranging
Toolbars and Windows
- Integrated
Development Environment
(IDE) contains
nine
different windows, all
of which can be docked, or anchored,
to other windows that are dockable
and four toolbars that that can be docked
or float in their own windows
- All windows can be resized
and located anywhere on the desktop
Design and
Run
Time
- Design time - when
application is built
- Run time - when
application is used
- Projects - applications (programs,
forms, and modules)
- Form - projects always start with a
form
Note: form becomes the window the
application occupies on desktop
- A project can have more than one form and
forms
created in one project can be used in other
projects (for these reasons, it is advisable to give
each form a unique name)
Form Properties
Adding and Removing
Controls
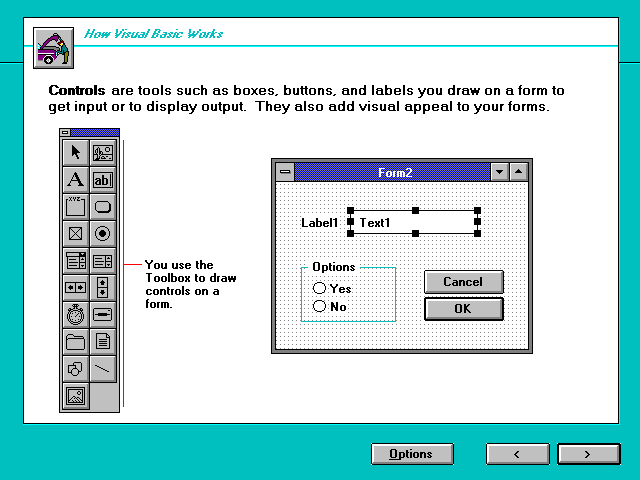 Controls - graphical images or objects
Controls - graphical images or objects- Toolbox - group of
tools in Visual Basic Window
Note: 20 intrinsic controls are in the Toolbox of Visual Basic’s
standard edition.
- 2000 Additional
controls available from
Microsoft and from third-party vendors
- 255 controls max allowed on each
form
3 Types of Controls
(Project One)
Removing
Controls
- Point to
Control
- Click
left mouse button
- Press DELETE key
Setting Properties
- Properties
- characteristics or
attributes
of a control
Note: set at design-time
by using the properties
window
- Default Values - initial values set by Visual Basic
Note: only change values that differ from the
default values
2 Sections of Properties
Window
- Object box - displays name
of control whose properties being set
- Properties list - displays set
of properties belonging to the control
(Two Tab sheets)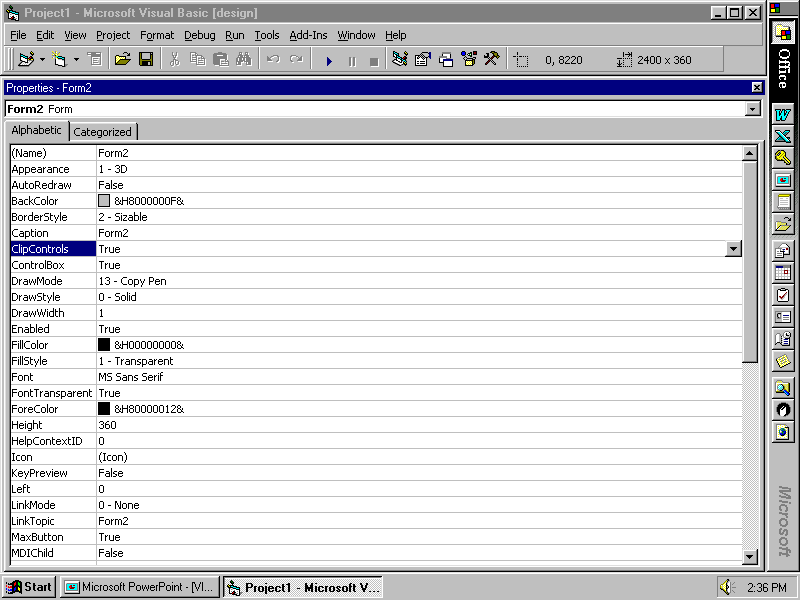
- Alphabetic
tab sheet -
lists the properties in alphabetic
order
- Categorized
tab sheet - groups
the properties by category
Property
Examples
Note: can be changed during
run-time
Property Examples
- Locked property - setting this property to
true prevents the user
from editing the contents of a text
box (used
to hold answer)
- TabIndex property -
determines the order
in which a control gets focus by tabbing
- TabStop property - setting this property to
false causes the focus to skip this
control
Naming Controls
Event
Procedures
Note: events can be the execution of
code statements at run-time
- Code - actions that will occur
within the application in response to
specific events
- language - Visual Basic words
and symbols used for computer instructions
Event
Procedures
Functions and
Methods
- Function - code that transforms
one or more values into a new value
example: Val
function takes whatever
value given and converts it to a number,
or zero if not possible
- Methods - code statements that
can be applied to an object
to change its attributes
or behavior
example: Setfocus
method causes focus to
be changed to a specific control on form (Text1.SetFocus)
Note: Visual
Basic has many
predefined functions and methods that you can
use in your code
Writing Code
Note: Each block has a header and terminal
statement to show where subroutine begins and ends
Note: These first and last
statements are supplied
by Visual Basic when you begin a new
event subroutine.
Subroutine Format
Sub Command1_Click ( )
‘Display Commission
Amount as val of UserInput * Rate
Text2.text = Val(Text1.text) * 0.15
Text1.SetFocus
End Sub
Note: Text in Blue supplied by Visual Basic
Coding Environment
- Text Editor - code window functions as a
text editor for
writing code statements (add and change options of Notepad)
- Interpreter - Visual Basic converts
your statements to binary as soon as ENTER key pressed.
Note: If statement can’t be
converted error
message displayed
Saving a Project
- Visual Basic projects
are saved as a set of files
- Forms
saved with extension .frm
- contains graphics,
additional .frx
file created
- Project saved with extension .vbp
- user specifies path
and filename using Save File As dialog box and the
Save Project As dialog box
Documenting an
Application
3
Parts of Print Dialog Box
- Form
Image
- prints blank form
at design-time
- Code -
prints code for module
or entire project
- Form
As Text
- prints a list of all controls and property
settings that are different
from their default settings
Note: must first select current module
(form) or the entire
project before selecting parts to
print
Project 1
Building an
Application
END
Program Maturity Calculator
Requirements
Return
to IFS 110 class Notes Menu!



